Menu
-
-
F.A.Q
- How to identify genuine agarwood chip, natural or cultivated
- How to identify oil injection / absorption fake agarwood beads
- How to know if there are more than one oil in your oil
- How to make your wood bracelet or mala darker
- How to tell if an Agarwood bead sinks WITHOUT sinking it under water?
- How does back flow incense work and how do you burn it?
- Where to start if you don't know what agarwood is ?
- Why are you losing money if you buy seeds and plants?
- Which agarwood incense should I choose?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Agarwood Related Articles
- Shipping
-
SHOP - Agarwood
-
SHOP - Other Fragrant Wood
-
SHOP - Incense Holder and Burner
-
- FREE Oud Oil guide
- Testimonials
- "Why did you buy this?"
- Contact us
- About Us
- +61430284329
- Login
-
English


Think Wild Agarwood Is Superior? Think Again – Cultivated Vs Wild Agarwood
November 22, 2024 7 min read
I was fulfilling your order. Buzz buzzed, and my phone vibrated. It was a call from Whatapp.
“Hello, Trent speaking”
“What is the difference between wild and cultivated agarwood?”
I was about to explain but the customer kept going.
“Which one is better?”
“Why the price is so much different?”
So I politely told him I would answer him in writing as I could not do it in a 5-minute call.
This reminded me that I had so many similar questions in the past, so I will address these questions in this blog.
What is cultivated Agarwood?
Cultivated Agarwood is Agarwood that was harvested from infected Aquilaria trees from a plantation.
What is Induced Agarwood?
Induced Agarwood is another name for cutlivated Agarwood.
Induced agarwood is created using advanced techniques that "trick" Aquilaria trees into producing resin. By using fungal inducers, scientists can stimulate the tree to make agarwood without relying on the slow, natural process. This approach not only protects wild trees but also provides a steady supply of this precious resource.
How is cultivated Agarwood made?
The whole-tree agarwood-inducing technique has shown high efficacy in producing high-quality agarwood in cultivated trees. This method improves yield up to 28 times compared to traditional techniques (Liu et al., 2013).
There are many different methods in artificial induction, such as physically drilled holes, chemical and biological inducers, which have been pivotal in agarwood production from cultivated Aquilaria trees. These methods address sustainability and enhance quality (Azren et al., 2019).
What is wild Agarwood?
Wild agarwood is produced under natural conditions when Aquilaria or Gyrinops trees are wounded or infected, forming resin in the wood (Chen et al., 2017).
But what are natural conditions? I think the key is “without” human intervention.
How is wild Agarwood made?
Fungal Infections: When trees are naturally infected by fungi such as Phaeoacremonium parasiticum, it triggers resin production in the heartwood as a defense mechanism (Manohara, 2013).
Insect Infestation: Certain insects and their larvae can damage the tree, inducing resin formation. For example, ants and boring insects.
Physical damages: Natural injuries caused by falling branches, storms, or grazing animals can trigger resin accumulation.
Environmental Stress: Conditions such as drought, high winds, or extreme temperature fluctuations may stress the tree, initiating resin production.
Soil and Climate: Specific soil types, humidity levels, and temperatures in tropical regions like Southeast Asia support the natural occurrence of resin-inducing factors.That explains why Agarwood are found mainly in South East Asia ( Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Laos, China, Vietnam)
Hunters will need to identify these trees in the wild to cut them down. How do they identify?
Based on experiences and appearance.
Any experienced vendors will be able to identify wild agarwood quickly but if you ask how they do that, chances are they will not tell you unfortunately.
How do scientists identify Wild from Cultivated Agarwood?
| Method | Textbook Definition | How does it work? | Explaination |
|---|---|---|---|
|
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with PCA |
HPLC separates chemical compounds in a sample based on their interaction with a column, while PCA (Principal Component Analysis) analyses data patterns to differentiate samples. | Run a liquid sample through a column, collect data, and apply PCA to interpret patterns. | It is like using a ruler to measure chocolate chips in cookies to see if they are homemade or store-bought. |
| UPLC–ESI-QTOF-MS | UPLC–ESI-QTOF-MS uses liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify chemical profiles and unique markers in complex mixtures. | Separate and detect molecular components using chromatography and ionization techniques. | This is like a super-magnifying glass that finds tiny details in cookie crumbs. |
| DNA Barcoding | DNA barcoding analyzes genetic sequences to classify organisms or determine the origin of biological materials. | Extract DNA, sequence specific regions, and compare them to databases. | Imagine looking at a cookie recipe book to find out which bakery made it. |
| Metabolomics and Genetic Markers | Metabolomics studies chemical fingerprints, while genetic markers provide insights into species or sample origins. | Analyze metabolites and genetic markers using spectrometry and genetic techniques. | Think of finding tiny fingerprints left by cookies to know where they came from. |
| Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIR) | NIR uses infrared light to analyze materials' compositions based on how they reflect or absorb the light. | Shine infrared light on samples and analyze reflected signals to determine properties. | A magic flashlight shines on cookies to see how they glow and tells if they are real or fake. |
Is wild Agarwood better than cultivated Agarwood?
Ma, Huang, Fu, Qiao, and Li (2023) demonstrated that induced agarwood has a similar chemical composition to wild agarwood. These scientists went further
1. Chemical Composition: Almost the Same!Induced agarwood contains many of the same beneficial compounds as wild agarwood, including sesquiterpenes and chromones. These ingredients are responsible for its medicinal and antioxidant properties. While the resin content is slightly lower, it’s about 83% as rich as wild agarwood—an impressive similarity.
2. Powerful Health Benefits- Antioxidant Power: Both wild and induced agarwood fight harmful free radicals in the body. These free radicals can cause aging, inflammation, and diseases. Induced agarwood can neutralize 80-93% of these harmful molecules as effectively as wild agarwood.
- Brain Health: Induced agarwood helps inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme linked to Alzheimer’s disease. This makes it potentially helpful for improving memory and preventing cognitive decline.
- Diabetes Management: It can also slow down sugar absorption by inhibiting alpha-glucosidase, an enzyme involved in breaking down carbohydrates. This property makes it a great option for managing blood sugar levels.
Why is Induced Agarwood Important?
1. A Lifesaver for the EnvironmentWild agarwood is rare because only a small percentage of Aquilaria trees naturally produce resin. Overharvesting has endangered these trees, making sustainable alternatives like induced agarwood crucial. By creating agarwood artificially, we can reduce the pressure on wild populations.
Trade and Conservation Concerns: Overexploitation and illegal harvesting of wild agarwood have necessitated conservation efforts and regulations under treaties like CITES to control its trade (Espinoza et al., 2014).
2. Accessible and Affordable
Wild agarwood is extremely expensive, with high-quality resin costing up to $15,000 per kilogram. Induced agarwood offers a more affordable alternative while still delivering many of the same benefits, making it accessible to more people.
3. Versatile ApplicationsWhether used in perfumes, traditional medicine, or as incense, induced agarwood holds promise in the same industries that have historically relied on wild agarwood.
The Science Behind Induced Agarwood (cultivated Agarwood)
Creating induced agarwood involves inoculating trees with fungi that stimulate resin production. These fungi trigger the tree's defense mechanisms, leading to the production of resin rich in medicinal compounds. The process is faster, more controlled, and ensures consistent quality.
The Future of Induced Agarwood
Induced agarwood shows that science and nature can work hand-in-hand. By offering a sustainable and effective alternative to wild agarwood, it opens doors for new medicines, better skincare products, and luxurious fragrances without harming our planet.
As research continues, we may see even more ways induced agarwood can be used to improve our lives while preserving nature. It’s a small innovation with big potential—a win for humans and the environment alike.
What about Agarwood beads? Is Wild one better?
Beads are about spiritual, in short they are different, Some molecules are only available in Wild Agarwood and vice versa.
I cannot say Wild Agarwood is better than cultivated. Better in what?
Wild Agarwood is rarer than cultivated Agarwood because they are unsustainable. Once harvested, it might take ten of decades to form.
Yes, Wild Agarwood is more expensive because it is harder to get.
Think about the last time you can get your hand on wild rice or wild banana. Have you ever seen or heard of them?
In term of aroma, this is very personal and subjective. Many people said wild agarwood smells better. My opinion is maybe, just maybe. You have to try it to feel it.
At Grandawood, we have a good collection of oud oils. Many of those surpass the wild oils. And this feedback are not from me, but from our customers.
| Feature | Wild Agarwood Beads | Cultivated Agarwood Beads |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | High complexity in aroma and resin composition due to natural formation under diverse stress conditions. Unfortunately, human ability can only detect a few of these aromatic notes. You need to almost press your nose against the bead to smell. So the perception is wild agarwood beads have better quality (more resin) | Comparable resin quality when advanced techniques like fungal induction are used. Subtle aroma, but decent Agarwood resin. Recent advanced technology gives cultivated agarwood resin a boost. Some beads have excellent density of Agarwood. Check out our Kygarwood |
| Availability | Rare and limited due to overharvesting and strict trade regulations. | Abundant, as it is cultivated using sustainable methods. |
| Environmental Impact | Unsustainable harvesting threatens Aquilaria species in the wild. | Environmentally friendly due to reforestation and controlled farming. |
| Cost | Very expensive due to rarity and high demand. | Relatively affordable and accessible. |
| Sustainability | Limited sustainability, as wild harvesting leads to deforestation. | Highly sustainable, supporting conservation efforts. |
- Chen, Y., et al. (2017). Distinguish the Wild from Cultivated Agarwood by Using HPLC Combined with PCA. Published in the Asian Journal of Plant Science & Research. Link to study.
- Espinoza, E., et al. (2014). Distinguishing Wild from Cultivated Agarwood (Aquilaria spp.) Using DART-TOFMS. Published in Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. Link to study.
- Huang, M., et al. (2023). Quality Similarity Between Induced Agarwood by Fungus and Wild Agarwood. Published in Frontiers in Plant Science. Link to study.
- Tan, C., et al. (2019). Agarwood Induction: Current Developments and Future Perspectives. Published in Frontiers in Plant Science. Link to study.
- Liu, Y., et al. (2013). Whole-tree Agarwood-Inducing Technique. Published in Journal of Forestry Research. Link to study.
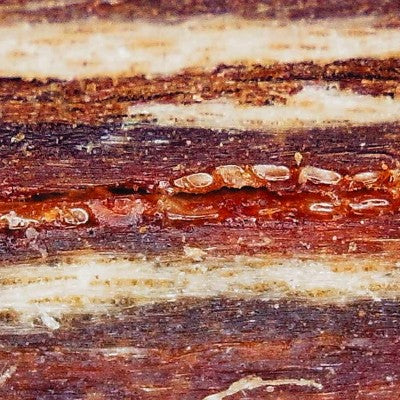
p/s Just to show you how good our cultivated GGG Agarwood beads are, I have 2 images
1) Phone Camera

2) Look closely how resinous it is

Final Thoughts:
Wild agarwood has an irreplaceable allure due to its rarity and complex aroma. To obgain wild Agarwood, there are many risks involved (image a 30-day journey to the jungle) This is the main reason for its high price. However, cultivated agarwood is a sustainable and innovative solution that balances quality, accessibility, and environmental responsibility. For consumers, the choice depends on personal preferences and priorities, such as cost, sustainability, and aroma.
At Grandawood, we offer a range of oud oils and cultivated agarwood products that are often rated superior to wild oils by our customers. Try them to experience the difference for yourself.
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.