Menu
-
-
F.A.Q
- How to identify genuine agarwood chip, natural or cultivated
- How to identify oil injection / absorption fake agarwood beads
- How to know if there are more than one oil in your oil
- How to make your wood bracelet or mala darker
- How to tell if an Agarwood bead sinks WITHOUT sinking it under water?
- How does back flow incense work and how do you burn it?
- Where to start if you don't know what agarwood is ?
- Why are you losing money if you buy seeds and plants?
- Which agarwood incense should I choose?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Agarwood Related Articles
- Shipping
-
SHOP - Agarwood
-
SHOP - Other Fragrant Wood
-
SHOP - Incense Holder and Burner
-
- FREE Oud Oil guide
- Testimonials
- "Why did you buy this?"
- Contact us
- About Us
- +61430284329
- Login
-
English
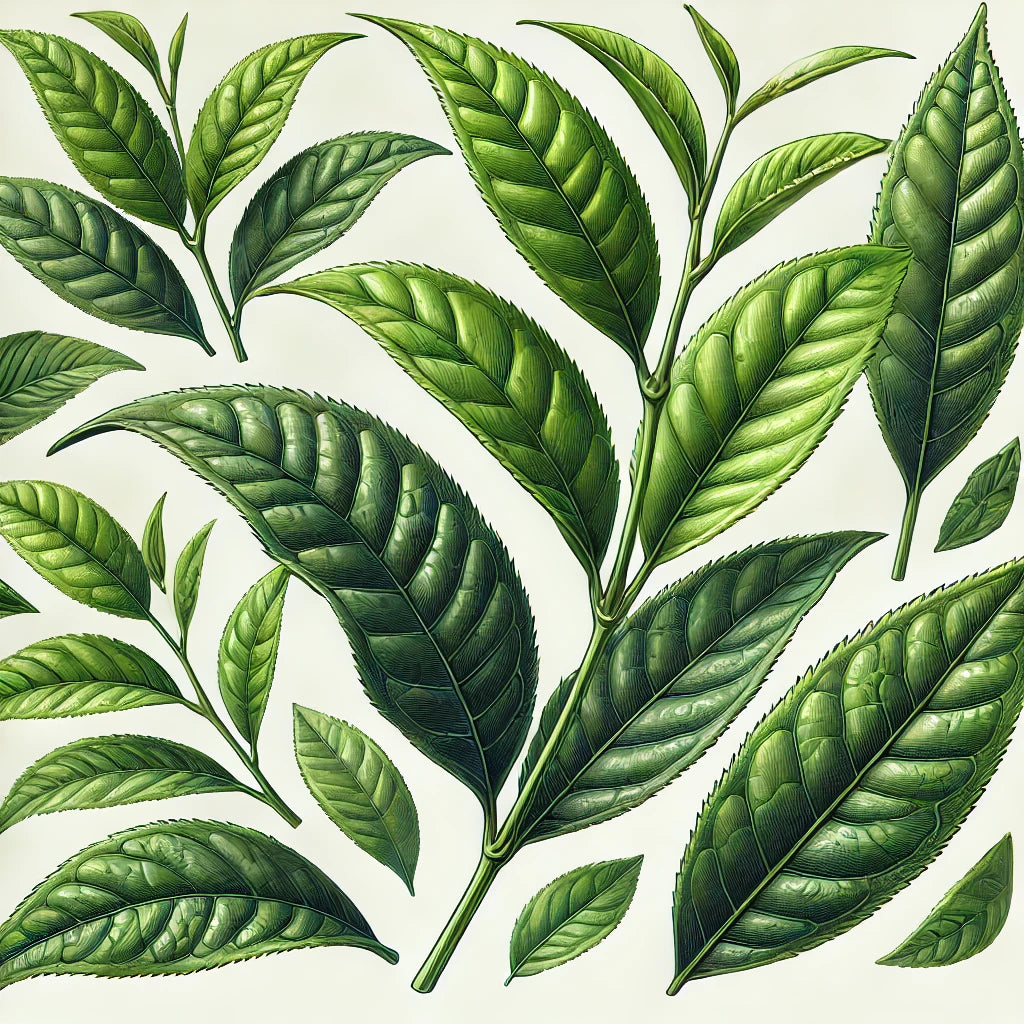


Agarwood tea (Aquilaria leaves) and Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis)
Understanding the Differences Between Aquilaria and Camellia Sinensis Leaves
The purpose of this entry is to highlight the differences in appearance between Aquilaria and Camellia Sinensis leaves. This is not intended to compare which leaf is better, as each has its own unique benefits.
Aquilaria
- Nature Leaves: Aquilaria leaves are elliptical in shape.
- Steamed Leaves: When torn, Aquilaria leaves reveal mini fibres or hairs between the torn parts.
Camellia Sinensis
- Nature Leaves: Camellia Sinensis leaves are also elliptical.
- Steamed Leaves: These leaves have a saw-toothed edge, making them distinguishable from Aquilaria leaves.
The Benefits of Green Tea and Aquilaria Leaves: A Scientific Overview
Green Tea Benefits
Green tea, derived from the Camellia sinensis plant, has been extensively studied for its numerous health benefits. The key bioactive components in green tea are catechins, which include epicatechin, epigallocatechin, epicatechin gallate, and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).
Health Benefits:
-
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties: Green tea is known for its strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which help in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer (Żuchnik et al., 2022).
-
Neuroprotective Effects: Regular consumption of green tea can support cognitive function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease (Saeed et al., 2017).
-
Cardiovascular Health: Green tea catechins have been shown to improve blood lipid profiles, reduce blood pressure, and enhance vascular function (Reygaert, 2017).
-
Weight Management: The catechins in green tea can boost metabolism and aid in fat loss, making it beneficial for weight management and obesity prevention (Xing et al., 2019).
-
Anti-carcinogenic Properties: Green tea polyphenols, particularly EGCG, have been found to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and prevent the spread of various types of cancer (Pervin et al., 2018).
Aquilaria Leaves Benefits
Aquilaria leaves, particularly from species like Aquilaria sinensis and Aquilaria crassna, have been traditionally used for their medicinal properties. Recent studies have started to uncover the scientific basis for their health benefits.
Health Benefits:
-
Lipid Metabolism Improvement: Feeding Aquilaria sinensis leaves to goats resulted in significant reductions in blood cholesterol levels and increases in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, suggesting similar potential benefits in humans (Min et al., 2023).
-
Cardiovascular Health: Aquilaria crassna leaf extracts have been found to act as vasodilators, improving vascular function without causing cytotoxicity, which indicates potential benefits for cardiovascular health (Wisutthathum et al., 2018).
-
Anticancer Properties: The ethanolic extract of Aquilaria malaccensis leaves has shown significant anticancer potential in in-vitro studies, indicating its usefulness in cancer treatment (Hegde et al., 2018).
-
Neuroprotection: Aquilaria crassna leaf extract has demonstrated neuroprotective effects and potential benefits in detoxifying harmful substances, which can aid in protecting neuronal cells and improving overall brain health (Pattarachotanant et al., 2023).
-
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties: The leaves of Aquilaria crassna are rich in antioxidants and have shown significant anti-inflammatory effects, making them useful in managing oxidative stress and inflammation-related conditions (Wongwad et al., 2019).
Conclusion
Both green tea and Aquilaria leaves offer a plethora of health benefits supported by scientific research. Green tea is particularly beneficial for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties, while Aquilaria leaves show promise in cardiovascular health, anticancer potential, and neuroprotection. Incorporating these natural compounds into your diet can contribute to overall health and well-being.
Visual Comparison
To illustrate these differences, please refer to the images below:
Aquilaria |
Camellia Sinensis |
||
| Nature leaves |
|
 |
|
| Steamed leave |  |
 |
|
Both are elliptical leaf but
Camellia Sinensis has a saw-toothed appearance.

Aquilaria leaves when torn, it will show mini fibre or hair between the torn part. To illustrate our point, please see the below images:


1 Response
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.






Fernando Surara
May 05, 2020
It was very informative.Please send and post related issues and topics of Aquilaria plants…Godspeed.