Menu
-
-
F.A.Q
- How to identify genuine agarwood chip, natural or cultivated
- How to identify oil injection / absorption fake agarwood beads
- How to know if there are more than one oil in your oil
- How to make your wood bracelet or mala darker
- How to tell if an Agarwood bead sinks WITHOUT sinking it under water?
- How does back flow incense work and how do you burn it?
- Where to start if you don't know what agarwood is ?
- Why are you losing money if you buy seeds and plants?
- Which agarwood incense should I choose?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Agarwood Related Articles
- Shipping
-
SHOP - Agarwood
-
SHOP - Other Fragrant Wood
-
SHOP - Incense Holder and Burner
-
- FREE Oud Oil guide
- Testimonials
- "Why did you buy this?"
- Contact us
- About Us
- +61430284329
- Login
-
English
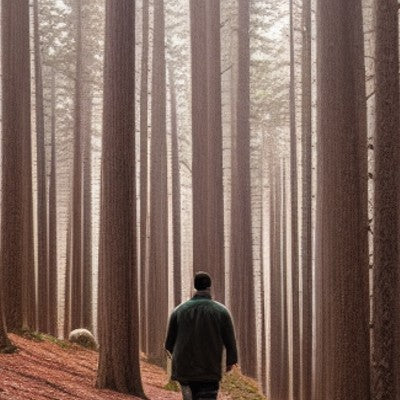


Agarwood and its mental health benefits
Table of Contents:[hide]
Biophilia Hypothesis
The biophilia hypothesis is that humans have an innate tendency to seek out and connect with nature and other life forms. This hypothesis was first proposed by psychologist Erich Fromm in the 1960s and has since been developed further by other scholars such as Edward O. Wilson.
There is a growing body of evidence that supports the biophilia hypothesis. For example, research has shown that exposure to nature can positively impact our physical and mental health. Studies have also found that contact with nature can help reduce stress levels, improve moods, and increase feelings of well-being.

The biophilia hypothesis provides a compelling explanation for why humans seem to be naturally drawn to nature. It also has important implications for how we design and manage our built environment. If we understand the importance of nature in our lives, we can make sure that our cities and towns are designed in ways that support our biophilia.
And it is also true the other way around. Nature's world will be better when receiving "love" from humans.
Reverse Biophilia Hypothesis?
One of the most famous examples of the biophilia hypothesis in action is the case of a Japanese physician, Dr Masaru Emoto. Dr Emoto was fascinated by the idea that human emotions could impact water molecules. To test his theory, he conducted an experiment exposing water to different words and emotions.
What he found was that the water molecules changed shape depending on the emotions that were directed at them. Water that was exposed to positive words and emotions formed beautiful, intricate crystals. In contrast, water that was exposed to negative words and emotions became disordered and chaotic.
Click here to learn more
Wilson's biophilia hypothesis includes the claim that, as a consequence of evolution, humans have an “innate tendency to focus on life and lifelike processes.
Wilson's biophilia hypothesis includes the idea that humans have an innate focus on life and things that are alive.
The relationship between the biophilia hypothesis and aromatherapy
The role of aromatherapy in reducing anxiety is evident, as research shows its power through animal and human trials. Its effects on anxiety are not fully understood, but scientists think that the GABAergic system is involved.
Some studies have shown that the scent of essential oils can be used to change how neurotransmitters work. This is done by targeting certain receptors. The purpose of this review is to explore the calming and sedative properties that come from different aromas. These include familiar scents like those found in coffee, tea, and whisky as well as other smells coming from food spices, volatile organic compounds, common botanicals and their ingredients. Furthermore, this Review will focus on how these particular aromas can target the GABAergic system to provide better anxiety treatment options.
Some evidence suggests that aromatherapy may benefit people suffering from anxiety or depression. Aromatherapy involves the use of essential oils, which are plant extracts that contain natural aromatic compounds. These compounds can be inhaled or applied to the skin and are thought to have various psychological and physiological effects.
Some research suggests that certain essential oils may have antidepressant or anti-anxiety properties. For example, one study found that lavender oil effectively reduced anxiety levels in a group of dental patients. Another study found that chamomile oil may help reduce symptoms of depression.
In many cultures, people have always tuned in to our unique connection with nature. For instance, the Japanese practice of shinrin-yoku, or ‘forest bathing’ is defined as immersing oneself in the natural atmosphere of the forest
Li says that shinrin-yoku means more than just being physically present in the forest – it means connecting with nature through all our senses and letting it fill us up.
Multiple Japanese studies have found that being in nature has emotional, physiological and restorative benefits, as well as improved work performance when compared to being in an urban environment. Some of the positive health outcomes from spending time in nature include lowered blood pressure, reduced muscle tension and increased brain wave activity in the alpha frequency.
Researchers studying the effects of forest bathing discovered that both male and female subjects had noticeably lower urine adrenaline and noradrenaline concentrations. Other studies have revealed that Forest bathing also reduces saliva cortisol levels, prefrontal cerebral activity and blood pressure in humans, and stabilises autonomic nervous system activity.
A study recently found that Forest bathing significantly increases Natural Killer (NK) activity. NK cells are a type of white blood cell that help the body fight off infections and diseases. In addition, forest bathing also increased the levels of intracellular anticancer proteins such as perforin, GRN and GrA/B. Li suggests that regular forest bathing may have a preventative effect on cancer generation and development
A study showed that spending two 2-hour stretches in the forest, with one walk being on consecutive days, increased the number and activity of anticancer NK cells by 50% and 56%. Even a month after returning to an urban lifestyle, these activities were still significantly high – 23% higher than before taking the walks. In addition, it was found that extended time spent in nature decreased inflammatory cytokines linked to chronic disease by nearly half. There was no such effect from Urban walks (Kuo M 2015)
Phytoncides
Phytoncides are plant-produced compounds that have an effect (usually protective) on another organism . Forest trees and plants emit volatile substances such as α-pinene, cis-3-hexenol (leaf alcohol), and β - thujaplicin. It is common knowledge that walking in the forest with the scent of phytoncides induces anxiety and sedative reduction. Aoshima and Hamamoto conducted a study focusing on the effects of these Phytoncides GABA A receptors, which are known to be expressed in Xenopus oocytes (or cells found within eggs). The study found that phytoncides have a positive effect on GABA responses- meaning that they have anxiolytic and sedative activity.
GABA is an amino acid that helps to keep the central nervous system calm. The GABAergic system is responsible for releasing and binding GABA as a neurotransmitter. The GABAergic system helps regulate how alert we are, how anxious we feel, how tense our muscles are, and whether or not seizures happen. It also helps with some memory functions.

The researchers produced aromatic volatile substances (phytoncides) by vaporizing Chamaecyparis Obtusa (hinoki cypress) stem oil with a humidifier in the hotel room during the night stay. They then took blood samples on the last day and analysed urine samples every day during the stay. They measured NK activity, the percentages of NK and T cells, and granulysin, perforin, granzyme A/B-expressing lymphocytes in blood, and the concentrations of adrenaline and noradrenaline in urine.
They took measurements of the number of phytoncides in the hotel room air on a normal working day before the stay for comparison. Phytoncide significantly increased the activity of natural killer cells, as well as the percentages of these cells that expressed perforin, granulysin, and granzyme A/B. Additionally, phytoncide exposure decreased the percentage of T cells and the concentrations of adrenaline and noradrenaline in urine samples. They found phytoncides, like u-pinene and -pinene, in the air of hotel rooms. This suggests that exposure to phytoncide may lead to higher NK activity by reducing stress hormone levels.
Li's research has proven that people who
- NK activity significantly increased, enhancing the activity of anticancer proteins. This, in turn decreased levels of stress hormones, increased the hours of sleep and decreased anxiety, aggression, fatigue and mental confusion.
- The pleasant mood stimulation also significantly lowered blood pressure by suppressing sympathetic nervous system activity and increasing parasympathetic nervous activity.
Evergreen trees, such as pine and cedar, naturally produce high levels of phytoncides. According to Li, we can replicate these results by diffusing essential oils.
The chemical makeup of phytoncides differs from tree to tree. Japanese hinoki cypress, Chamaecyparis obtusa, is the most common type in Japan and its dominant scent comes from the following chemicals: d-limonene, α-pinene, β-pinene and camphene 5
Why am I writing this?
Because my family is Agarwood farmer
so I would like to show you how Agarwood can be helpful to mental illness
How can Agarwood be beneficial to mental illness?
The Agarwood tree is a resinous and fragrant wood that comes from the Aquilaria trees. This resin is produced due to an infection or injury to the agarwood tree's stem. Since ancient times, religious texts such as Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, and Islam have held it in high regard. In 65 B.C.E., Dioscorides documented several medical uses for this substance.
For centuries, agarwood has been used in Traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine to treat various conditions, including inflammation-related disorders, joint pain, and anxiety. It is also known to have sedative and cardioprotective effects. Agarwood oil is used in many popular fragrances and incense, and research has shown that it can have an effect on the nervous system.
Agarwood, also known as 'bad-energy-removing wood', has been used in ancient Chinese literature for its traditional ability to remove negative energy and promote wakefulness. The wood is usually heated or burned to produce a fragrant smoke that is believed to improve sleep quality. Agarwood oil has also been shown to help treat mental illnesses, mainly anxiety, depression, and insomnia.

Burning Agarwood incense brings calming and spiritual mood. Diffusing Agarwood oil could release "human natural killer cell (NK) activity".
Human natural killer cells are a type of white blood cell that play a role in the innate immune system. These cells help to identify and eliminate Infected or cancerous cells. Natural killer cells are lymphocytes that help to protect the body from tumours and infections. They work by stopping the tumours or infections from spreading and doing damage to other tissues in the body (Viver et al 2008)
The reason:
Agarwood oil is rich in sesquiterpenes (more than 100 sesqiterpenes) which are aromatic volatile substances.
Li et al (2009) stated it was not clear what kind of factors in the forest environment activated human NK Cells, but he and his fellow researchers thought that aromatic volatile substances derived from trees, including monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, called phytoncides.
Diffusing Agarwood oil will release sesquiterpenes in the air, so it means in theory, it would help human body to produce more NK cells.

Below is the summary of Chen et al 2022
Anti-Anxiety Effects
Anxiety disorders are characterized by a general feeling of unease, worry or fear. This can accompany physical symptoms such as sweating, heart palpitations, trembling and dizziness. People with an anxiety disorder may avoid situations that make them feel anxious and may also experience difficulty sleeping or concentrating.
Anxiety disorders are caused by a decrease in neurotransmitters, which leads to a dysfunction of the neurotransmitter system.
Repeatedly restraining mice caused them to become anxious, but administering AEO (Agarwood essential oil) helped relieve their anxiety.
The light-dark exploration (LDE) experiment increased the residence time of mice in the light chamber, and it was found that AEO had a significant anxiolytic effect.
Anti-Depressant Effects
There are many ways that people can become depressed. It can be caused by a chemical imbalance in the brain, it can be brought on by stressful life events, or it can be a combination of both. Whatever the cause, depression is a serious condition that should not be taken lightly. If you or someone you know is showing signs of depression, it is important to get help as soon as possible.
Depression can manifest itself in several different ways. Some people may withdraw from social activities and isolate themselves. Others may become more irritable and snap at those around them. People with depression may also have trouble concentrating or sleeping, and may lose interest in things
The main antidepressants used today are monoamine reuptake inhibitors, but they are ineffective for half of the depressed patients.
Wang showed that a certain dose of Agarwood Essential Oil (20 and 40 mg/kg) had efficacy comparable to paroxetine (10 mg/kg) in Tail Suspension and Forced Swimming experiments conducted on stressed mice. By reducing the immobility time, it was surmised that AEO has good antidepressant efficacy according to Wang's tests.
When Wang observed the behavioural changes of the Twenty Flavored Agarwood Pill on desperate mice, they discovered that it was able to shorten the immobility time of TS and FS experiments and alleviate depressive symptoms.
Huang separated 40 depressed patients into two groups:
- The control group received standard therapy (psychological guidance and antidepressant medication)
- The treatment group was treated with agarwood fumigation therapy.
The agarwood fumigation treatment was based on lighting incense twice a day in both groups for 2 weeks as a course of treatment, for a total of two courses of treatment.
The results showed that the treatment group’s total effective rate was 85%, and the control group’s total effective rate was 55%.
It showed that aromatherapy was effective in improving the clinical symptoms of depressed patients and reducing the CES-D (Depression Scale) and HAMD (Hamilton Depression Scale) scores, with good clinical effects.
Agarwood incense was found to be an effective treatment for reducing symptoms of depression.
Sleep-Promoting Effects
Insomnia may be caused by stress and the dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex system or by dysregulation of central neurotransmitters.
Sedative-hypnotic drugs are a class of depressants that can be used to treat insomnia.
Agarwood extracts (aqueous, alcoholic, and volatile oils) were used by Wang to synergize the suprathreshold and subthreshold hypnosis experiments with sodium pentobarbital. It was found that agarwood extract and AEO significantly increased the sleep rate and prolonged sleep time in mice compared to the blank group. In addition, it was found that the AEO also significantly shortened the sleep latency in mice. These findings suggest that agarwood extract and AEO have strong sedative-hypnotic effects.
Another study found that agarwood incense significantly increases the amount of sleep in mice.
Small, medium, and large doses of agarwood significantly shortened sleep latency and increased sleep time in mice when administered via inhalation, with the medium dose also increasing the number of animals that slept under subthreshold conditions. . Liang used normal mice and insomnia mice induced by PCPA (300 mg/kg) and investigated the effects of agarwood incense inhalation on sleep and mood by various behavioral assays . The results showed that the inhalation of agarwood incense (0.3 g for 6 mice and 0.5 g for 6 mice) significantly promoted the sleep of normal mice and significantly improved the quality of life and motor ability of insomniac mice. After a few weeks of taking diazepam and AEO, the laxative effect wore off on the group administered with only diazepam. However, there was no significant drug resistance in those who took agarwood.
By dividing 120 insomnia patients into two groups, with one group receiving nightly fumigation with agarwood and the other group receiving fumigation with propanol that did not affect sleep, Lei discovered that those who received agarwood slept significantly better and had less severe symptoms of anxiety and depression.
In light of the studies cited above, we can infer that AEO (Agarwood essential oil) has a mild-to-severe soporific effect with hardly any side effects and no reports of drug resistance. Consequently, AEO is a sleeper's dream come true for those seeking an alternative therapy to fight insomnia.
To summarise, AEO has profound sedative and tranquillising effects (anxiolytic, antidepressant, and pro-sleep). Additionally, several of its monomeric compounds - such as benzyl acetone, calarene, and jinkoh-eremol - have significant central nervous system activity. This may be the material basis for the sedative and tranquillizing effects of AEO. With this in mind then, these substances have the potential to be developed into new psychotropic drugs.
Associated Neurotransmitter Changes
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate communication between nerve cells in the central nervous system.
Inadequate GABA in the brain can keep neurons in a state of impulsive excitation for an extended period of time, which is one of the major causes of physiological insomnia.
Agarwood essential oil has been found to improve PACA-induced insomnia by increasing the levels of Monoaminergic neurons (regulate many functions of the Central Nervous System), GABA and reducing Glutamate, which helps you to sleep.
GABA is the main chemical that stops messages from passing between nerve cells in your brain. Glutamate is the main chemical that allows messages to be carried between nerve cells.
The study found that Agarwood essential oil has sedative-hypnotic effects due to its ability to promote the synthesis and release of GABA, and increase the expression of GABAA receptors.
Wang found that Oud essential Oil promotes the synthesis and release of GABA, which may have sedative-hypnotic effects.
The levels of neurotransmitters and their metabolites in the brain are thought to be associated with the onset of psychiatric disorders.
Inadequate GABA in the brain can keep neurons in a state of impulsive excitation, which is one of the major causes of physiological insomnia.
The sleep-promoting effect of AEO was blocked by the competitive antagonist flumazenil.
The sedative and sleep-promoting effect of the essential oil was mainly through regulating the GBBAergic system.
Agarwood may show sedative and antidepressant effects due to elevated serum serotonin level.
Kynam affects the dopaminergic, 5-hydroxytryptaminergic, GABAergic, long-term depression, and neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions pathways in mouse brains.
Neuroprotective Effect
Yang found that seven chromones isolated from agarwood expressed significant neuroprotective activity and greatly improved cell survival in glutamate-induced and corticosterone-induced P12 chromophobe cells and human U251 glioma cells, while the compound 6,8-dihydroxy-2-[2-(30-hydroxy-40-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]chromone exhibited neuroprotective activity comparable to that of the positive drug fluoxetine, with an 82.2% and 86.9% increase in cell viability for both types of cells, respectively
The researcher found that agarwood compounds have neuronal protective activity.
Associated Neurotransmitter Changes
The sleep-promoting effect of AEO (Agarwood Essential Oil) was blocked by the competitive antagonist flumazenil.
The sedative and sleep-promoting effect of the essential oil was mainly through regulating the GBBAergic system.
Agarwood may show sedative and antidepressant effects due to elevated serum serotonin levels.
Kynam affects the dopaminergic, 5-hydroxytryptaminergic, GABAergic, long-term depression, and neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions pathways in mouse brains.
Antioxidant Effect
The oxidative stress hypothesis is the most accepted theory for the cause of central degenerative diseases.
The treatment of PC12 cells with AEO significantly reduced oxidative damage in PC12 cells.
Lee found that agarwood alcohol extract helped reduce oxidative damage in the hippocampus of mice that were repeatedly stressed. This showed that agarwood alcohol extract has a neuroprotective effect on oxidative damage in the hippocampus. . Agarwood extracts can help scavenge free radicals, inhibit oxidative stress, and protect cells from death. This was shown in a study involving mice with isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction.
Anti-Inflammatory Effect
Inflammation is your body's natural response to infection or injury. It might sound bad, but it is actually a good thing when you're injured because it helps your body heal.
Inflammation is a process by which the body's white blood cells and the substances they produce protect us from infection with foreign organisms, like bacteria and viruses. However, sometimes inflammation can become chronic, meaning it lasts for longer than it should. This can happen when the immune system mistakes healthy cells and tissues for being foreign and begins to attack them.
Some believe that chronic inflammation can be the root cause of various health issues, such as heart disease, arthritis, depression, Alzheimer's disease and cancer.
To reduce damaging inflammation that can lead to chronic diseases, eat anti-inflammatory foods and avoid those that promote it. Triggers for this condition include red meat, refined carbs like white bread or pastries,, fried foods, and sugary beverages. A better alternative is to consume green leafy vegetables and fruits, nuts, fatty fish, and olive oil. Furthermore, ensure you are getting enough exercise and sleep, as well as keeping your stress levels in check.
Agarwood has excellent anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. According to Li, The ethanolic extract of agarwood had a significant inhibitory effect on the swelling of mouse ears when exposed to xylene and could effectively improve the increase in capillary permeability caused by acetic acid in mice.
Furthermore, many sesquiterpenes and chromones isolated from Agarwood showed anti-inflammatory activity.
That explains why some people feel relaxed and calm when diffusing Agarwood essential oil.
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity
Acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme that helps to break down acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a chemical that is important for transmitting messages between nerve cells. When acetylcholinesterase is inhibited, it means that the enzyme cannot do its job as well, and message transmission can be disrupted. This can lead to various problems, including muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, and even death. Inhibiting acetylcholinesterase is a common way to kill pests like insects and rodents since it interferes with their nervous systems. Some chemicals that are designed to do this are called "insecticides" and " herbicides." However, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors can also be helpful to humans. For example, they are used to treat conditions like Alzheimer's disease and myasthenia gravis. When used properly, they can help improve symptoms and quality of life.
Inhibition of this enzyme can lead to increased levels of acetylcholine, resulting in improved muscle function and increased nerve activity. Various compounds have been found to inhibit acetylcholinesterase, and these compounds are being studied for their potential therapeutic benefits.
Several of the chemicals that make up agarwood, such as sesquiterpenes and chromones, have shown to be effective in inhibiting acetylcholinesterase.
Yang found that among the monomeric compounds isolated from A. crassna , three epoxy-2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones had significant acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity . Wei Li counted at least 69 compounds isolated from agarwood with varying degrees of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity.
Agarwood evidently contains a significant quantity of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, which makes it a promising candidate for treating neurodegenerative diseases.
In summary, Agarwood has various potential health benefits, including reducing oxidative damage and inflammation and promoting relaxation and calm.
1 Response
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.


Allyne Rosenthal
January 05, 2024
Hi, You cite several research studies that validate and explain the scientific basis for agarwood effectiveness. Is it possible to get the actual citations? I appreciate the thoroughness of your article.