Menu
-
-
F.A.Q
- How to identify genuine agarwood chip, natural or cultivated
- How to identify oil injection / absorption fake agarwood beads
- How to know if there are more than one oil in your oil
- How to make your wood bracelet or mala darker
- How to tell if an Agarwood bead sinks WITHOUT sinking it under water?
- How does back flow incense work and how do you burn it?
- Where to start if you don't know what agarwood is ?
- Why are you losing money if you buy seeds and plants?
- Which agarwood incense should I choose?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Agarwood Related Articles
- Shipping
-
SHOP - Agarwood
-
SHOP - Other Fragrant Wood
-
SHOP - Incense Holder and Burner
-
- FREE Oud Oil guide
- Testimonials
- "Why did you buy this?"
- Contact us
- About Us
- +61430284329
- Login
-
English
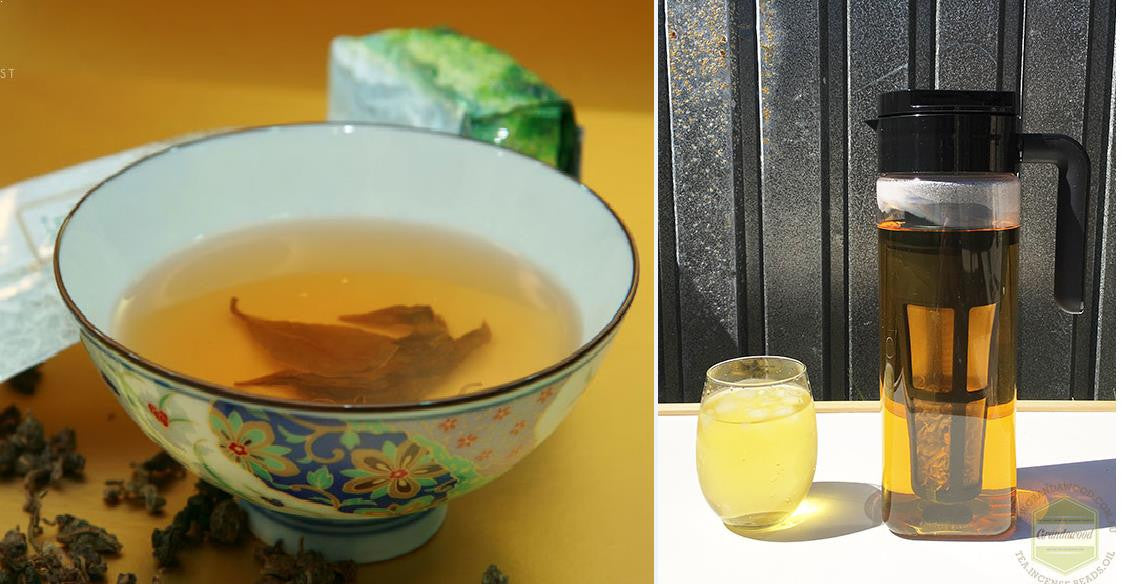


Agarwood teas benefit : A 2016 research, Neurology and Aquilaria Crassna Leaves
June 13, 2017 1 min read
Agarwood (Aquilaria) leaves have been consumed as a beverage for health promotion in many countries. In the past few years, Aquilaria Crassna leaves have been studied further due to their potential in antioxidative, antibacterial, antipyretic, analgesic, and laxative activities (for past research click here). Supasuteekul (et al 2016)'s and his team research show that these leaves are the sources of neuritogenic and neuroprotective constituents, which may be processed as a natural supplement or functional foods for neurodegenerative disorder prevention such as age related chronic diseases: : Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease
The above table is the lab test result of our agarwood leaves which have the same compounds in this study by Supasuteekul, Tadtong, Putalun, Tanaka, Likhiwitayawuid, Tengamnuay and Sritularak (2016, Journal of Food Biochemistry)
Through chromatographic techniques, three phenolic glycosides were isolated from the leaves of Aquilaria Crassna:
1) Genkwanin 5-O-β-primevoside
2) Iriflophenone 3,5-C-β-D-diglucoside
3) Iriflophenone 3-C-β-D-glucoside
Compounds 1 and 2 have been identified as the active components responsible for the neuroprotective and neuritogenic properties of Aquilaria Crassna. Nevertheless, the precise mechanisms behind their neuroprotective effects require further research.
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.